Methane
Separation, purification and liquefaction of small volumes of methane
Methane (CH₄) is the simplest saturated hydrocarbon in composition. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it one of the most cost-effective energy sources, as well as an accessible raw material for the chemical industry, although its capture, transportation and storage are difficult, since at standard temperature and pressure it is a gas.
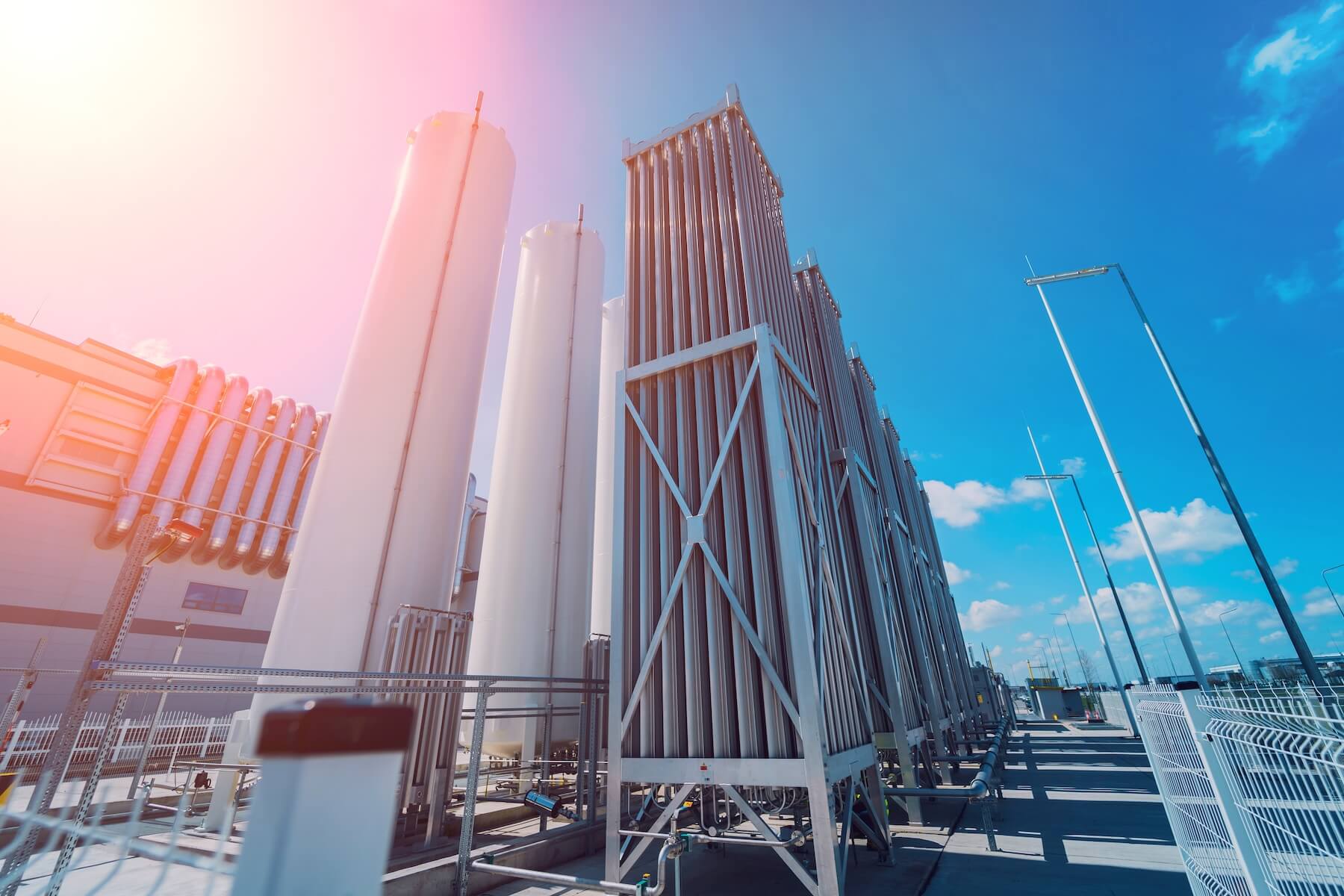

The main sources of methane for industry are associated with firstly, oil and natural gas, which is produced by developing oil and gas fields, and secondly, biogas, which is released during the fermentation of biomass.The cheapest way to transport large volumes of methane is pipeline transport, where the gas under the pressure of 75 atmospheres moves through pipes with a diameter of up to 1.4 meters.The laying of gas pipelines is very capital-intensive, and their construction for remote or low-flow methane sources is economically unjustified. In such cases, an alternative technology is used: methane is cooled to a liquid state (methane in this state of aggregation is called LNG) at a temperature of about -160°C (the volume is reduced by 600 times), and then, under slight excess pressure, it is transported to the consumer in cryogenic tanks by road, rail or sea transport.The technology of purification and liquefaction of small volumes of methane is in demand in the following industries:
Biogas
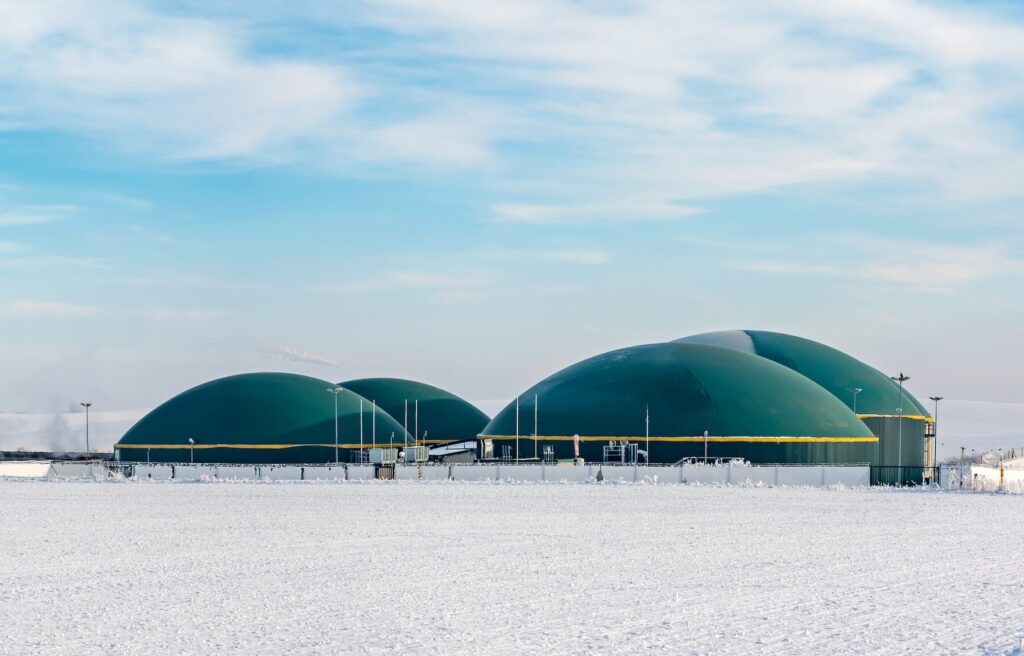
Biogas, derived from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter such as agricultural waste, food waste, manure and sewage sludge, contains a significant amount of methane. Traditionally, biogas plants burn this methane to generate electricity. However, as Feed-In Tariffs (FITs) — which subsidize electricity production from renewable sources — ends in the coming years, many biogas plants are seeking alternative ways to remain profitable:
-
Participation in tenders for the conclusion of the next FIT -
Construction of a biogas purification complex and subsequent connection to the gas transmission system -
Construction of a biogas purification and biomethane liquefaction complex -
Non-standard solutions (biogas purification and biomethane compression, use as raw material for industrial production, etc.) -
Closing the production facility
But not all biogas plants will be able to connect to the central gas transmission system (due to restrictions on geographical distance from the GTS, terms for obtaining permission from regulatory authorities and documentation for connection, the need for additional investments in bringing biogas to biomethane standards and connecting it to the GTS) and participate in tenders for the next FIT (subsequent tariffs are significantly lower than the current ones, a limited number of industry participants meet the criteria).The integration of a NANO Methane Purification & Liquefaction Plant will be the most cost-effective solution for most biogas producers

Flare gas
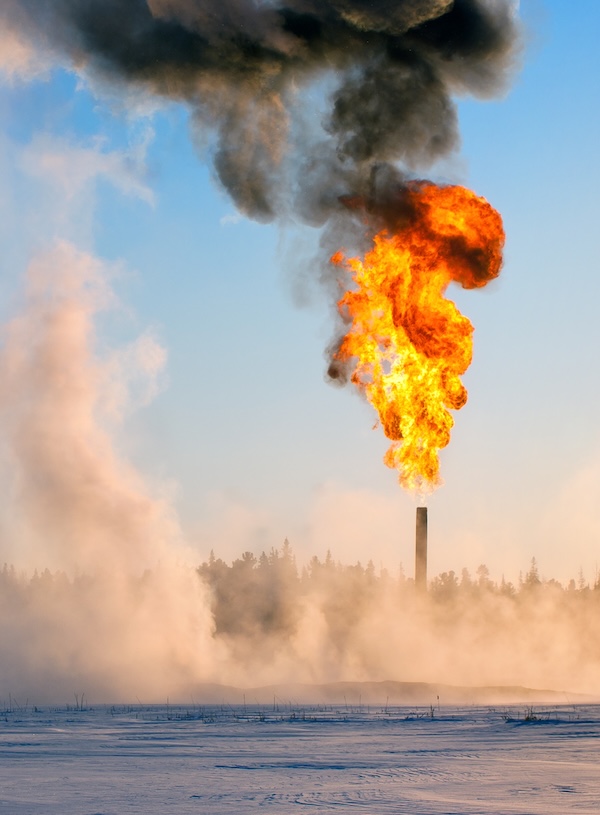
The process of oil production and preparation is most often accompanied by the emission of associated petroleum gas (APG), which consists of light hydrocarbons, primarily methane. For a long time, it remained a by-product for oil companies, the problem of its utilization was solved simply – by flaring. But this method of utilization leads to environmental pollution and increases the global greenhouse effect. In most developed countries, flaring is also fined by the government.The global oil and gas production industry is quite fragmented, there are thousands of small and medium-sized production companies operating individual or small groups of wells. For them, the volume of associated petroleum gas itself is not enough to justify the costs of infrastructure required to connect to gas pipelines or transport gas to existing processing plants.Therefore, for such small production companies, a cost-effective solution is the processing and liquefaction of flare gas directly at the oil field using a NANO Biomethane Liquefaction Module.

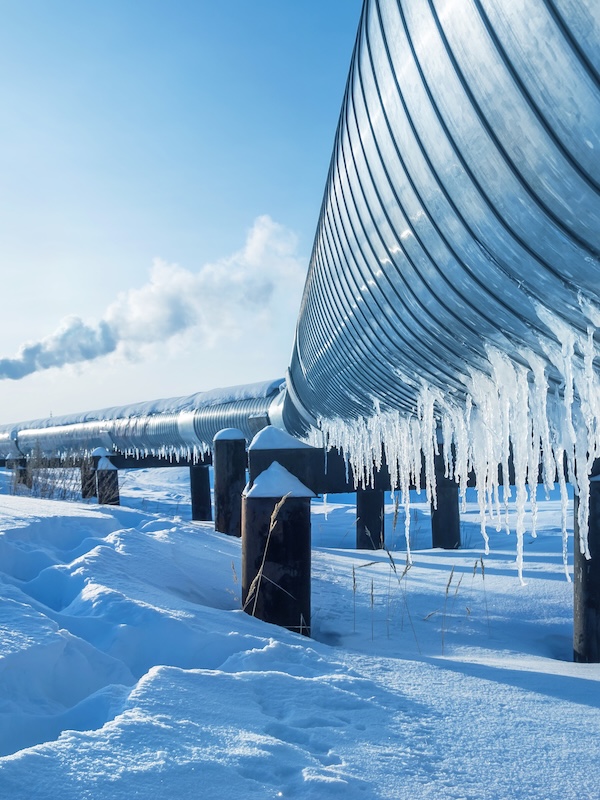
Gas Grid
Liquefaction of small volumes of methane from the gas network allows to significantly expand the geography of natural gas supplies and create a flexible infrastructure for its use, especially in areas where the construction of gas pipelines is technologically impossible or economically inexpedient.Delivery of motor fuel to sparsely populated areas and areas remote from oil refining centers significantly increases its cost. If there is a gas transportation network in the region, the construction of the NANO Biomethane Liquefaction Module can become a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for the local motor transport infrastructure.
In gasified regions, in the event of interruptions in the supply of natural gas through gas pipelines, the production of small volumes of LNG can provide cogeneration facilities (joint production of electricity and heat) with backup fuel to temporarily maintain operation or cover peak loads during periods when the demand for electricity and heat increases significantly.Liquefying small volumes of methane from gas pipelines thus helps develop a more flexible, reliable and sustainable regional energy system that supports the growing demand for clean fuels worldwide.

Application
LNG is rapidly becoming the preferred fuel for heavy-duty transportation, especially for trucks, buses, and other large vehicles, as municipalities and logistics companies shift towards cleaner energy solutions. The push for sustainability across the European Union, alongside the need for cost-effective fuel solutions, has led to widespread adoption of LNG. Moreover, BioLNG, a carbon-negative form of LNG produced from organic waste, and manure is emerging as a critical fuel source for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and meeting stringent environmental targets.
Benefits
Lower Emissions, Especially with BioLNG
One of the most significant advantages of LNG, and especially BioLNG, is the drastic reduction in emissions. LNG vehicles emit up to 25% less CO₂ than diesel-powered vehicles. When using BioLNG, the environmental benefits are even greater, as it can be carbon-negative—capturing more carbon during production than it emits during combustion. This makes BioLNG a powerful tool for achieving net-zero emissions and helping municipalities and companies meet their environmental commitments. Additionally, LNG produces far lower emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and almost no particulate matter, improving air quality and reducing public health risks.
Cost Efficiency
LNG is approximately 30% cheaper than diesel, providing significant cost savings for both municipalities and logistics companies that operate large fleets. The affordability of LNG is driving many organizations to make the switch, as fuel costs are a major component of operational expenses. The long-term financial savings from using LNG or BioLNG, coupled with the reduced maintenance costs due to cleaner combustion, make it an attractive option for fleet operators.
Fuel Efficiency
LNG is over 20% more efficient than diesel, meaning that vehicles can travel farther on a single refueling. This is a game-changer for long-haul trucking and public transportation systems, where maximizing range and minimizing refueling stops is crucial for operational efficiency. Logistics companies, in particular, are finding LNG’s superior fuel efficiency to be a major advantage, improving route optimization and reducing overall transportation costs.
Alignment with EU Sustainability Goals
The European Union has set ambitious sustainability goals, and LNG, especially BioLNG, is a key component in reducing carbon emissions from transportation. BioLNG, produced from organic waste such as agricultural byproducts and food waste, is a renewable and sustainable energy source that can help municipalities and logistics companies contribute to the EU’s carbon neutrality targets by 2050. The ability to use BioLNG allows these sectors to drastically reduce their carbon footprint while continuing to operate efficiently.
Growing Adoption by Logistics Companies
Logistics companies, which are responsible for moving goods over vast distances, are increasingly turning to LNG and BioLNG to reduce both costs and emissions. With long-haul trucks running on BioLNG, logistics firms can capitalize on the fuel’s carbon-negative properties, reducing their environmental impact and meeting stricter emission regulations. This adoption is also driven by the cost savings associated with LNG’s lower price and superior fuel efficiency.